Module 9: Engineering and Design in ASEAN
Table of Contents
Reading Text & Presentation
9.3 Mechanical engineering
9.3.1 Basic knowledge
Broadly speaking, mechanical engineering is an engineering discipline that uses engineering, physics, and materials science principles for the analysis, design, manufacture, and maintenance of mechanical systems. It involves the production and usage of heat and mechanical power for the design, production, and operation of machines and tools. Engineers in this field should have an understanding of some or all of these concepts: mechanics, kinematics, thermodynamics, materials science, structural analysis, and electricity. These core principles and their associated tools (including computer-aided design nowadays), design and analyze manufacturing plants, industrial equipment and machinery, heating and cooling systems, transport systems, aircraft, watercraft, robotics, medical devices, weapons, and other engineering fields.
In this part of the module we will look at the mechanical engineering of the motor car.
Even a basic automotive engineer needs to have a good training background. Some of the courses a mechanical engineer would cover are statics, dynamics, solid mechanics, thermodynamics, heat transfer, vibrations, and controls. Once an engineer has this ground knowledge they should be able to get to grips with a car engine.
9.3.2 Car engines: Basic engine parts
- Cylinder
The core of the engine is the cylinder, with the piston moving up and down inside the cylinder. The engine described above has one cylinder. That is typical of most lawn mowers, but most cars have more than one cylinder (four, six and eight cylinders are common). In a multi-cylinder engine, the cylinders usually are arranged in one of three ways: inline, V or flat (also known as horizontally opposed or boxer).
Different configurations have different advantages and disadvantages in terms of smoothness, manufacturing cost and shape characteristics. These advantages and disadvantages make them more suitable for certain vehicles.
- Spark plug
The spark plug supplies the spark that ignites the air/fuel mixture so that combustion can occur. The spark must happen at just the right moment for things to work properly.
- Valves
The intake and exhaust valves open at the proper time to let in air and fuel and to let out exhaust. Note that both valves are closed during compression and combustion so that the combustion chamber is sealed.
- Piston
A piston is a cylindrical piece of metal that moves up and down inside the cylinder.
- Piston rings
Piston rings provide a sliding seal between the outer edge of the piston and the inner edge of the cylinder. The rings serve two purposes:
- 1) They prevent the fuel/air mixture and exhaust in the combustion chamber from leaking into the sump during compression and combustion.
- 2) They keep oil in the sump from leaking into the combustion area, where it would be burned and lost.
Most cars that "burn oil" and have to have a quart added every 1,000 miles are burning it because the engine is old and the rings no longer seal things properly.
- 1) They prevent the fuel/air mixture and exhaust in the combustion chamber from leaking into the sump during compression and combustion.
- Connecting rod
The connecting rod connects the piston to the crankshaft. It can rotate at both ends so that its angle can change as the piston moves and the crankshaft rotates.
- Crankshaft
The crankshaft turns the piston's up and down motion into circular motion just like a crank on a jack-in-the-box does.
- Sump
The sump surrounds the crankshaft. It contains some amount of oil, which collects in the bottom of the sump (the oil pan).
- Ignition system
The ignition system produces a high-voltage electrical charge and transmits it to the spark plugs via ignition wires. The charge first flows to a distributor, which you can easily find under the hood of most cars. The distributor has one wire going in the center and four, six, or eight wires (depending on the number of cylinders) coming out of it. These ignition wires send the charge to each spark plug. The engine is timed so that only one cylinder receives a spark from the distributor at a time. This approach provides maximum smoothness.
- Engine cooling
The cooling system in most cars consists of the radiator and water pump. Water circulates through passages around the cylinders and then travels through the radiator to cool it off. In a few cars (most notably Volkswagen Beetles), as well as most motorcycles and lawn mowers, the engine is air-cooled instead (You can tell an air-cooled engine by the fins adorning the outside of each cylinder to help dissipate heat.). Air-cooling makes the engine lighter but hotter, generally decreasing engine life and overall performance.
- Air-intake
Most cars are normally aspirated, which means that air flows through an air filter and directly into the cylinders. High-performance engines are either turbocharged or supercharged, which means that air coming into the engine is first pressurized (so that more air/fuel mixture can be squeezed into each cylinder) to increase performance. The amount of pressurization is called boost. A turbocharger uses a small turbine attached to the exhaust pipe to spin a compressing turbine in the incoming air stream. A supercharger is attached directly to the engine to spin the compressor.
- Starting system
The starting system consists of an electric starter motor and a starter solenoid. When you turn the ignition key, the starter motor spins the engine a few revolutions so that the combustion process can start. It takes a powerful motor to spin a cold engine. The starter motor must overcome all the internal friction caused by the piston rings, the compression pressure of any cylinder(s) that happens to be in the compression stroke, the energy needed to open and close valves with the camshaft, and all of the "other" things directly attached to the engine, like the water pump, oil pump, alternator, etc.
Because so much energy is needed and because a car uses a 12-volt electrical system, hundreds of amps of electricity must flow into the starter motor. The starter solenoid is essentially a large electronic switch that can handle that much current. When you turn the ignition key, it activates the solenoid to power the motor.
- Fuel system
The engine's fuel system pumps gas from the gas tank and mixes it with air so that the proper air/fuel mixture can flow into the cylinders. Fuel is delivered in three common ways: carburetion, port fuel injection and direct fuel injection.
In carburetion, a device called a carburetor mixes gas into air as the air flows into the engine.
In a fuel-injected engine, the right amount of fuel is injected individually into each cylinder either right above the intake valve (port fuel injection) or directly into the cylinder (direct fuel injection).
In a diesel engine, there is no spark plug. Instead, diesel fuel is injected into the cylinder, and the heat and pressure of the compression stroke cause the fuel to ignite. Diesel fuel has a higher energy density than gasoline, so a diesel engine gets better mileage.
- Engine lubrication
Oil also plays an important part. The lubrication system makes sure that every moving part in the engine gets oil so that it can move easily. The two main parts needing oil are the pistons (so they can slide easily in their cylinders) and any bearings that allow things like the crankshaft and camshafts to rotate freely. In most cars, oil is sucked out of the oil pan by the oil pump, run through the oil filter to remove any grit, and then squirted under high pressure onto bearings and the cylinder walls. The oil then trickles down into the sump, where it is collected again and the cycle repeats.
- Exhaust system
The exhaust system includes the exhaust pipe and the muffler. Without a muffler, what you would hear is the sound of thousands of small explosions coming out your tailpipe. A muffler dampens the sound. The exhaust system also includes a catalytic converter. The emission control system in modern cars consists of a catalytic converter, a collection of sensors and actuators, and a computer to monitor and adjust everything. For example, the catalytic converter uses a catalyst and oxygen to burn off any unused fuel and certain other chemicals in the exhaust. An oxygen sensor in the exhaust stream makes sure there is enough oxygen available for the catalyst to work and adjusts things if necessary.
- Electrical system
The electrical system consists of a battery and an alternator. The alternator is connected to the engine by a belt and generates electricity to recharge the battery. The battery makes 12-volt power available to everything in the car needing electricity (the ignition system, radio, headlights, windshield wipers, power windows and seats, computers, etc.) through the vehicle's wiring.
(Source: Adapted from http://auto.howstuffworks.com/engine2.htm retrieved 24/03/2014)
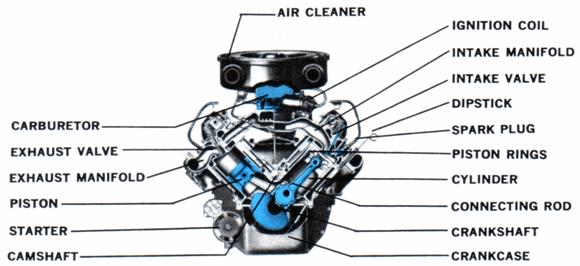
Parts of a 4-cylinder car engine
Langquage Focus 9.3
Activities